Chamonix Mont Вlanc (Department of Haute Savoie) 1035 – 3300 m – a classic year-round sports and mountain (and ski) resort in France – sports and recreation in the mountains in winter and summer in the Alps ..
Chamonix-Mont-Blanc or simply Chamonix is a commune and city in the department of Haute-Savoie in the Auvergne-Rhone-Alpes region, the site of the first Winter Olympic Games in 1924. As of 2017, 8611 people lived in it.
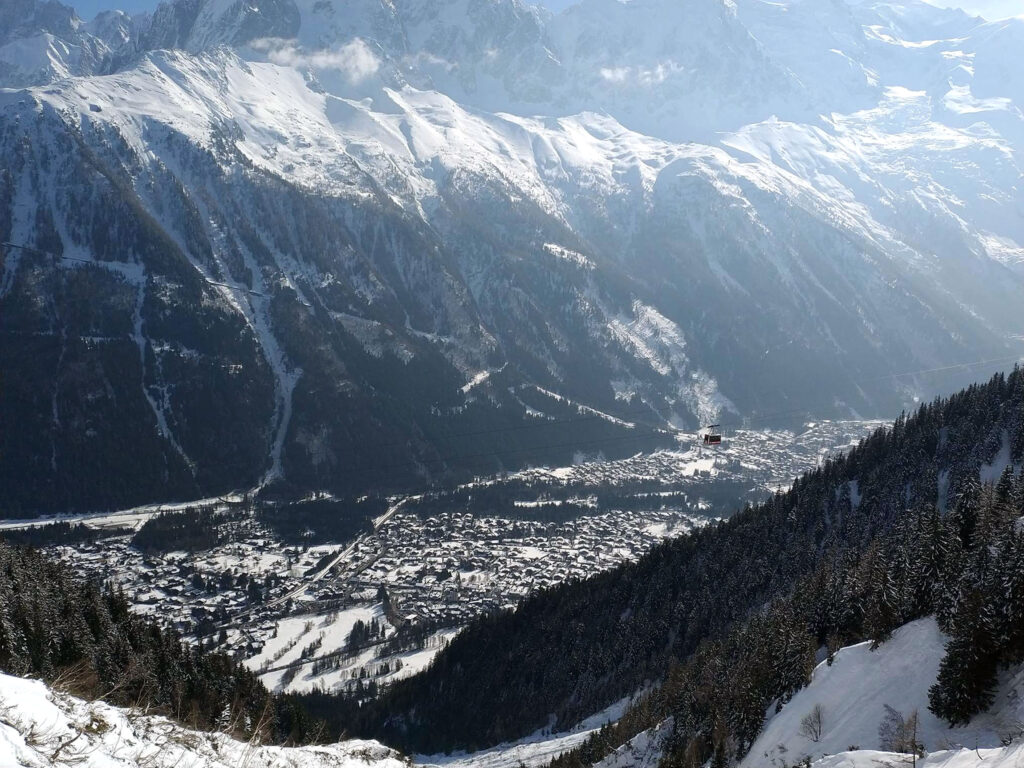
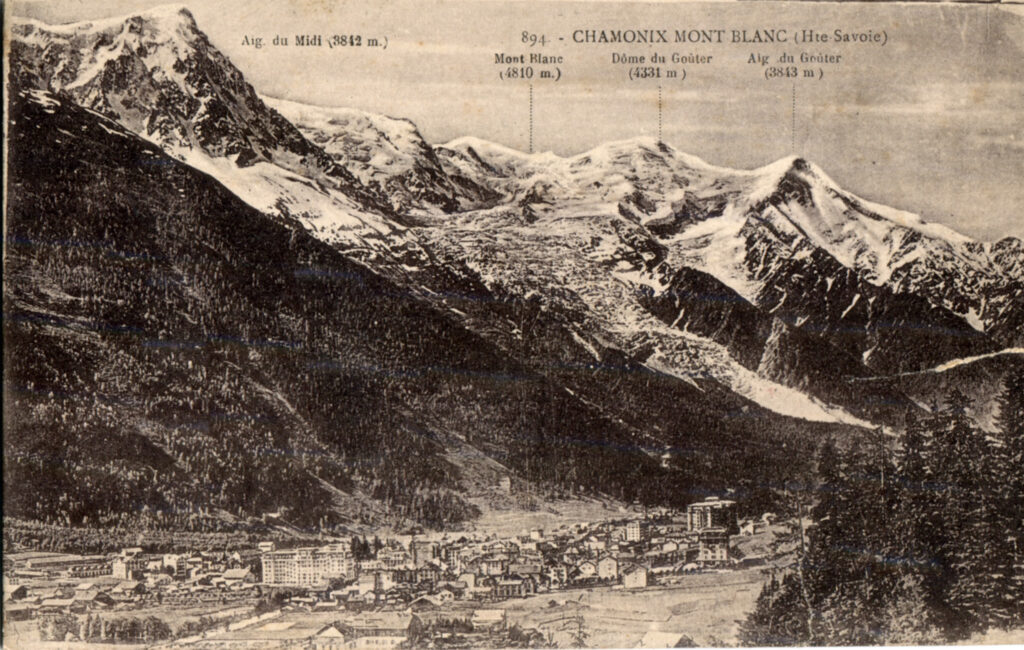
Chamonix is one of the oldest ski resorts in France, located north of Mont Blanc, between the peaks of the Aiguilles Rouges and the famous peak of the Aiguille du Midi. The commune of Chamonix is popular with skiers and mountain lovers; The Aiguille du Midi cable car takes you to the off-piste (remote) ski run of Vallee Blanche.
Chamonix is the “capital” of skiing. It is not surprising that this resort receives many foreign guests. The cradle of skiing, hosting the first Winter Olympics in 1924, offers ski slopes of exceptional quality, like those of the Verte des Houches. Chamonix, with a magnificent view of the top of Mont Blanc, is the ideal place for both beginners and experienced skiers.
Photogallery of views of the early 20th century, collection of the “Union of Taxi Drivers in Paris and Nice” (C)
- Chamonix Mont Blanc Valley, Alps
- View of the valley and resort Chamonix Mont Blanc, Alps
- Hiking in the mountains with a guide
- Mountain peaks in Chamonix
A little history of the resort and the city. The valley was first mentioned in 1091, when the Count of Geneva gave it to the great Benedictine house of Saint-Michel de la Cluse, near Turin, who founded a monastery here by the beginning of the 13th century. However, in 1786, the inhabitants bought their freedom from the canons of Sallanches, to whom the monastery was transferred in 1519.
In 1530, the inhabitants received from the Count of Geneva the privilege of holding two fairs a year, while the valley was frequented by civil officials and the Bishops of Geneva (the first recorded visit was in 1411, while Saint Francis of Sales did not arrive there until 1606). .). But travelers for pleasure were very rare. Chamonix was part of the historical land of Savoy, which emerged as a feudal territory of the House of Savoy in the 11th-14th centuries. The historical territory is divided between the modern countries of France, Italy and Switzerland. The House of Savoy became the longest surviving royal house in Europe. He ruled the County of Savoy until 1416, and then the Duchy of Savoy from 1416 to 1860. The first party to publish (1744) an account of their visit was the account of Richard Pocock, William Wyndham and others, such as the English visiting the Merde -Glace (Mer de Glace) in 1741. In 1742, P. Martel and several other Genevans arrived, in 1760, Horace-Benedict de Saussure, and later Marc Theodor Burri.
The growth of tourism in the early 19th century led to the formation of the “Compagnie des Guides de Chamonix” in 1821 to regulate access to the mountain slopes (which were publicly or jointly owned), and this association held a monopoly of leadership from the city until it was abolished by the actions of the French government in 1892; thereafter guides had to hold a diploma issued by a commission dominated by civil servants and members of the French Alpine Club rather than locals.
Since the late 19th century, tourism development has been dominated by national and international initiatives rather than local entrepreneurs, although the local community has become increasingly dependent on the tourism industry and has become increasingly active.
World War I. The commune successfully lobbied to change its name from Chamonix to Chamonix-Mont-Blanc in 1916. However, after losing its monopoly, the Compagnie transformed itself into the Association of Local Guides and retained an important role in the local society, providing its members with the services of a friendly society, and in the 20th century many of them were famous climbers and popularizers of mountain tourism, especially the writer Roger Frison-Roche, the first member of the company not born in Chamonix.
Olympic Games. The hosting of the first Winter Olympics in Chamonix in 1924 further enhanced Chamonix’s prestige as an international tourist destination.
During World War II, an orphanage operated in Chamonix, in which several dozen Jewish children took refuge from the Nazis. Some of those who hid them were recognized as Righteous Among the Nations.
By the 1960s, agriculture was reduced to a minimum, while the number of available tourist beds increased to about 60,000 by the end of the 20th century, with about 5 million visitors a year.
Chamonix in summer. Sports, festivals and holidays.
In summer, Chamonix becomes one of the most popular resorts in the French Alps. Hiking, cycling, festivals and much more.
Information about hotels and attractions can be found on the resort website www.chamonix.fr
Chamonix, youth and boy scouts.
Chamonix is one of the best all-season mountain resorts in France. Thanks to the railway, this resort became one of the first accessible to the public. Youth organizations around the world, especially scouts, began to periodically use Chamonix-Mont-Blanc for mountain hikes and sports activities in winter and summer. Chamonix is also well suited for families with children or youth holidays in the mountains.
Practical information.
How to get there.
Public transport. Railway. Shuttle Buses.
– Geneva International Airport. Meeting, private transfer, English-speaking taxi, sightseeing tours
Hotels, shelters.
The sights of France on old postcards – the collection of the Union of Taxi Drivers in Paris.